坐落于长江之滨,武汉是中国中部自古以来的通都大邑。享“九省通衢”之美名,今日的武汉依旧是经济与交通重镇,并持续开拓不断发展。在国家政策的支持下,武汉快速增长的科技创新力量,将引领中国下一波的发展浪潮。
Wuhan’s strategic location on the banks of the Yangtze River in central China has led to its sustained success as a trade hub for centuries. Heralded as the “crossroads of nine provinces,” Wuhan continues to build on this legacy of economic vitality and mobility. Boosted by a series of national policies and already revered as one of the world’s fastest growing hubs for technology and innovation, the city is advancing its ambition to be at the vanguard of China’s next wave of progress.
▼场地现状包括武汉高铁站、主要道路基础设施、水利渠道及北洋桥垃圾填埋场 Existing conditions on the site include the high-speed rail station, significant roadway infrastructure, channelized canals, and a solid waste landfill.
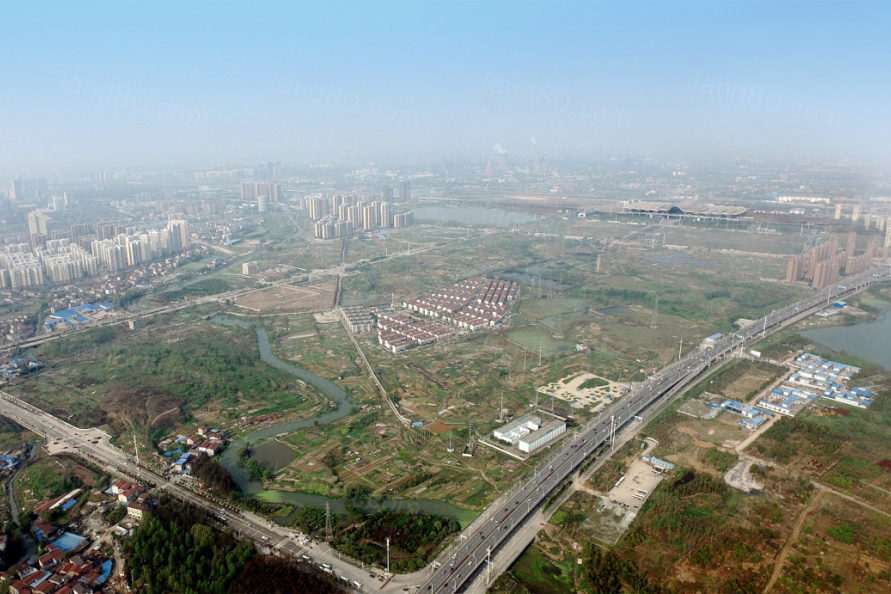

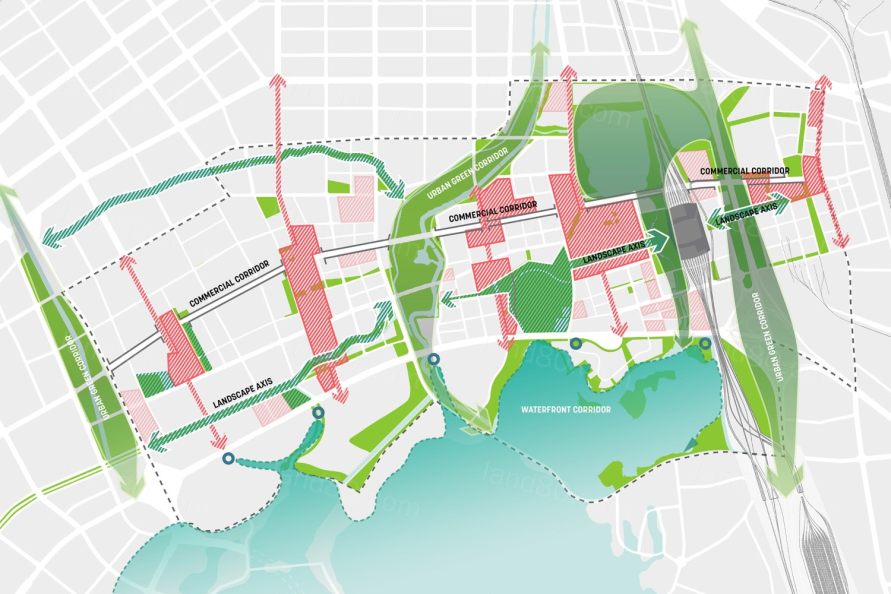
▼一系列的组织原则回应了区域内的现状议题,确立了核心的设计策略 A series of organizing principles summarize the issues impacting the district and define key design strategies.
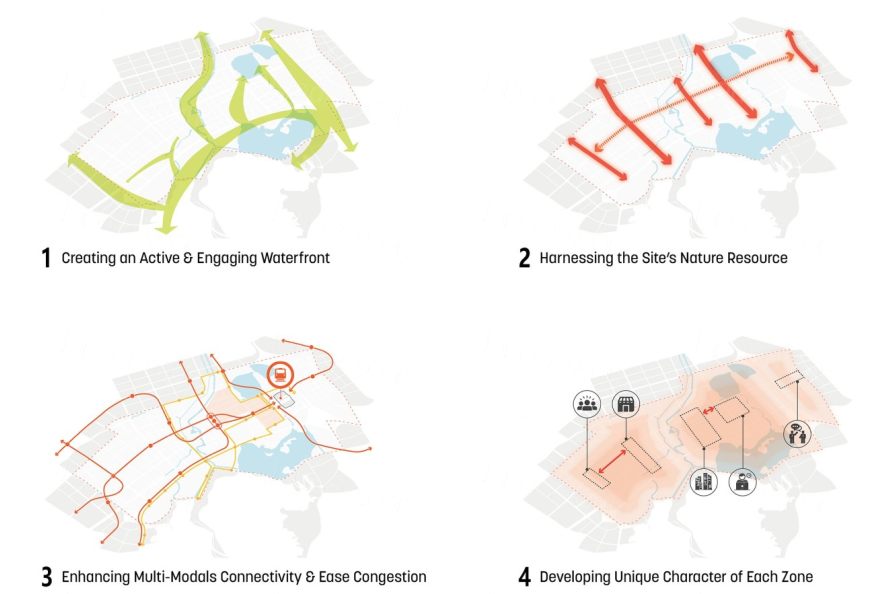
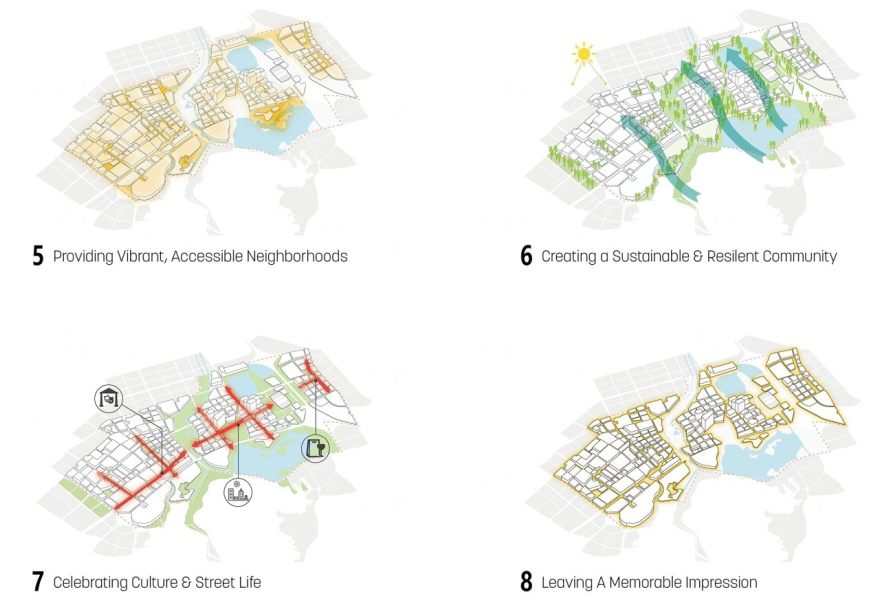
▼通过景观的介入,设计创建了联系开放空间和开发地块的组织框架 Major landscape interventions establish an armature of connected open spaces and development parcels.
▼区域占地约1800公顷,其中包括368公顷的公共开放空间,提供了多样化的休闲娱乐设施和诸多生态效益 The 1,800 hectare district includes 368 hectares of public open space that provides diverse recreational amenities and a host of ecological benefits.
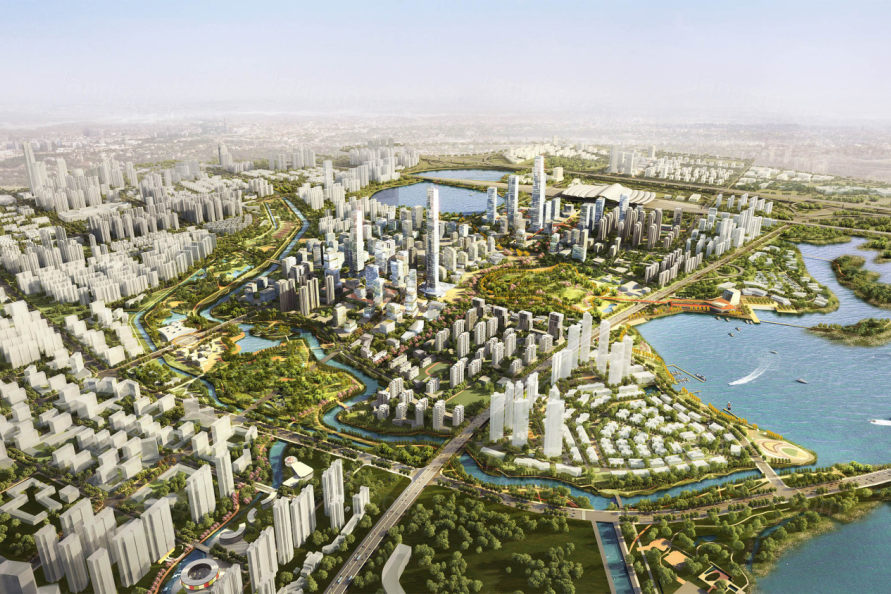

▼区域彩色平面 Illustrative Master Plan of the entire district.

▼中央公园周围的开发项目鸟瞰 Aerial view of the development surrounding the central park.
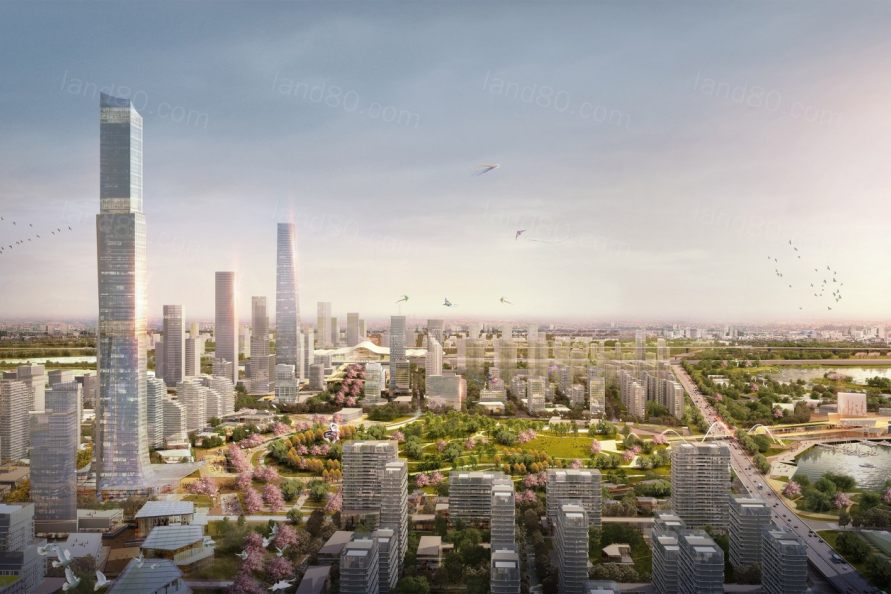

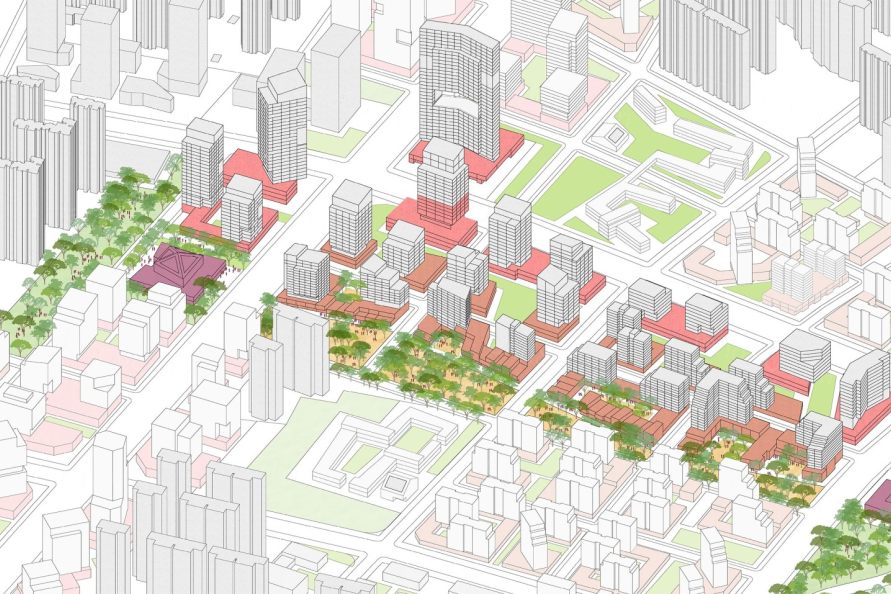
▼建筑的排布最大化利用景观格局,在区域内创造城市地标 Buildings are organized to take advantage of views and to create landmarks within the district.
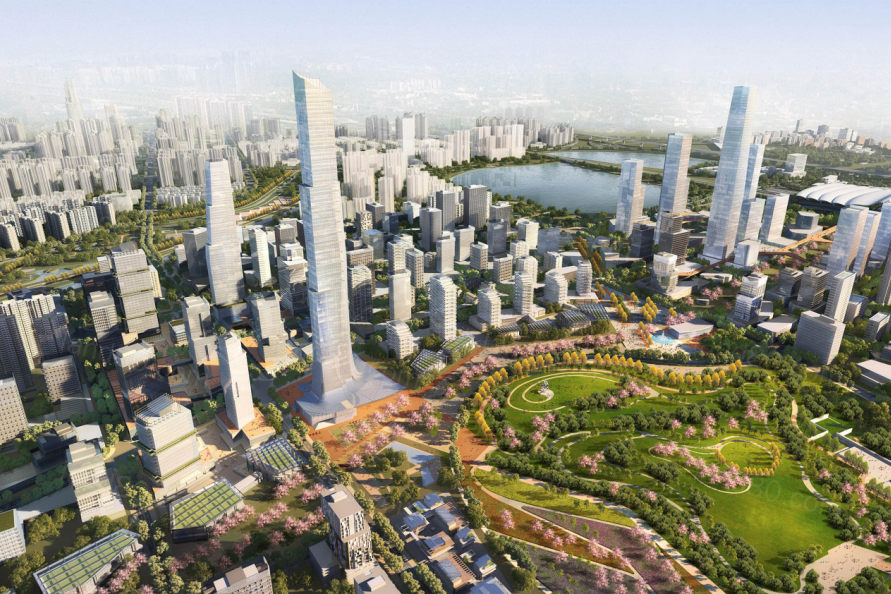

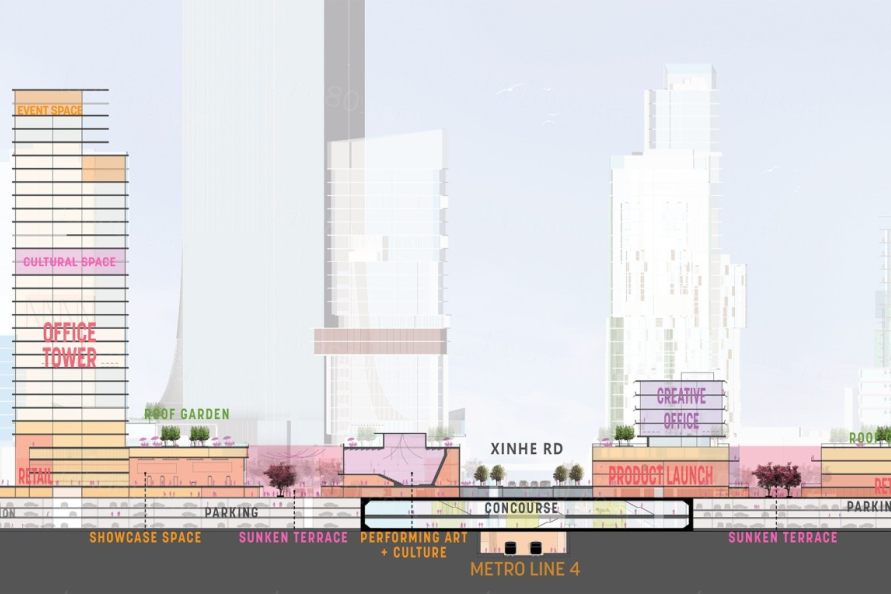
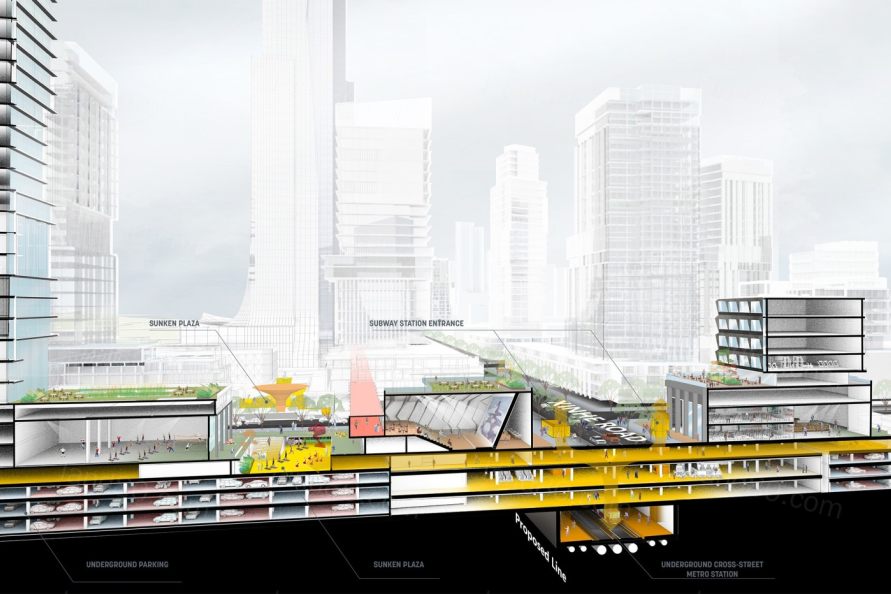
▼信和路商业主干道剖面 Section through the main commercial spine.
中国高速铁路网络的迅速铺开,强力驱动着全国城市与区域的发展。杨春湖高铁商务区紧邻武汉高铁站,城市发展与高铁交通的耦合,正是中国高铁举措成功的典型案例。Sasaki联合奥雅纳(Arup),仲量联行 (JLL)以及武汉市规划研究院的跨学科团队, 共同推进高铁商务区的规划设计。近期,本规划正式通过了市级决议,标志着武汉在实现商务区美好愿景的道路上,迈出了坚实且富有远见的一步。
The rapid expansion of China’s High Speed Railway network has been instrumental in driving economic growth throughout the country at both the city and regional scale. Evidence of this initiative’s success is the pairing of the Wuhan High Speed Railway station and the new Yangchun Lake Business District. Designed by Sasaki in collaboration with a diverse interdisciplinary team including Arup, JLL, and the Wuhan Planning & Design Institute, the master plan was recently approved by the city, marking a major step forward as Wuhan embraces a progressive yet realistic vision for the district.
▼核心区面向中央公园,并通过商业走廊连接高铁站 The mixed-use core fronts onto a central park and with a commercial spine linking to the high-speed rail station.
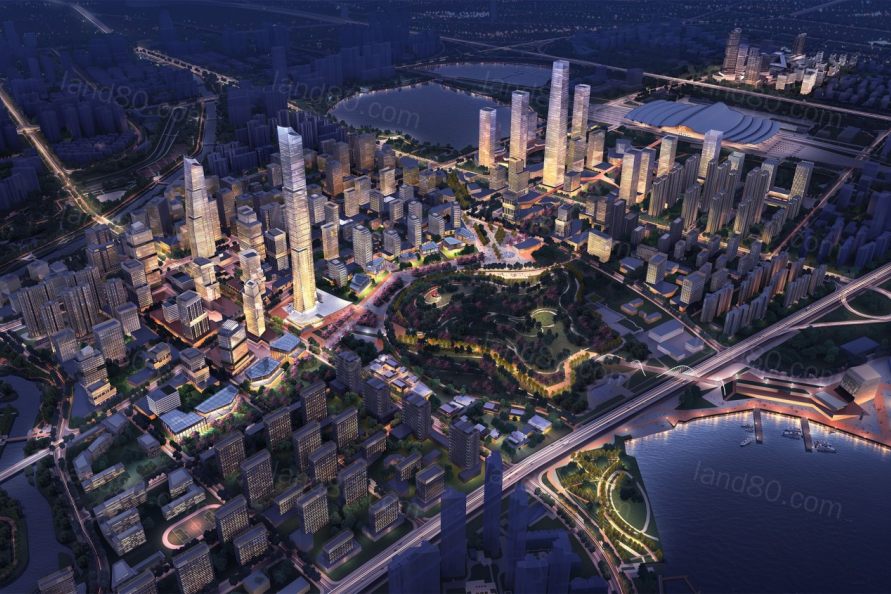

▼商业主干线强调了与高铁站的连接,并优先考虑步行路线 The commercial spine emphasizes the connection to the high-speed rail station and prioritizes pedestrian routes.
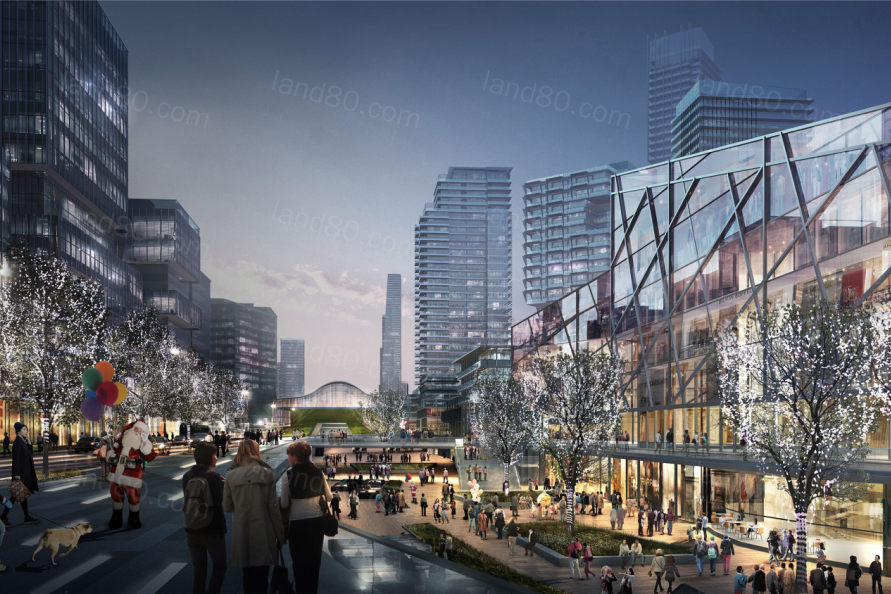

▼地铁出站空间的统一设计,为开发商提供了更多的可租面积,也为行人提供了地块间穿行的便捷路径 Interstitial space between subway tunnels and surface roadways are an opportunity for additional leasable space and pedestrian connections between urban blocks.
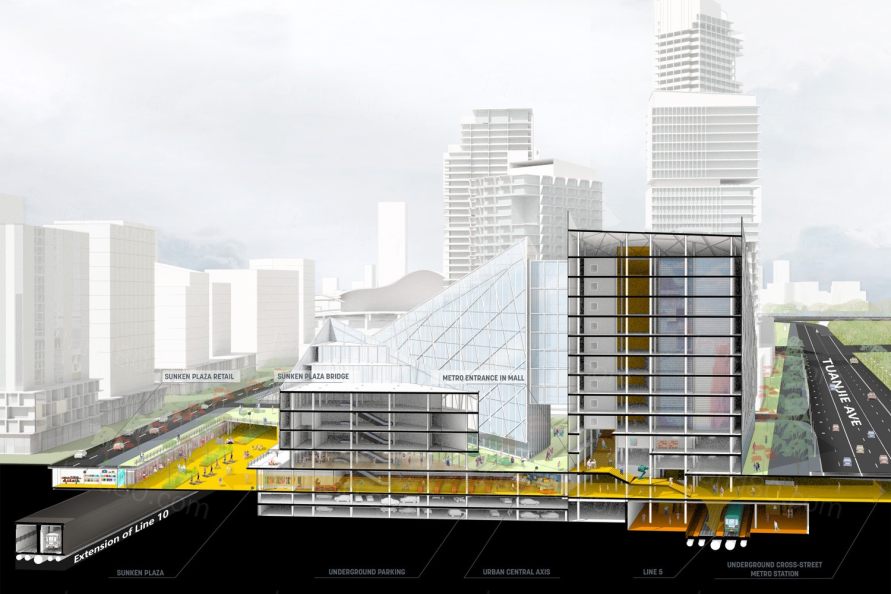

▼多层次的公共空间,为人们提供了多样的户外体验,从下沉式的商业广场到餐厅、咖啡馆露台,再到尺度宜人口袋公园,应有尽有 A layered public realm provides multiple spaces for people to interact with the outdoors ranging from sunken retail plazas to restaurant and café terraces to intimate pocket parks.
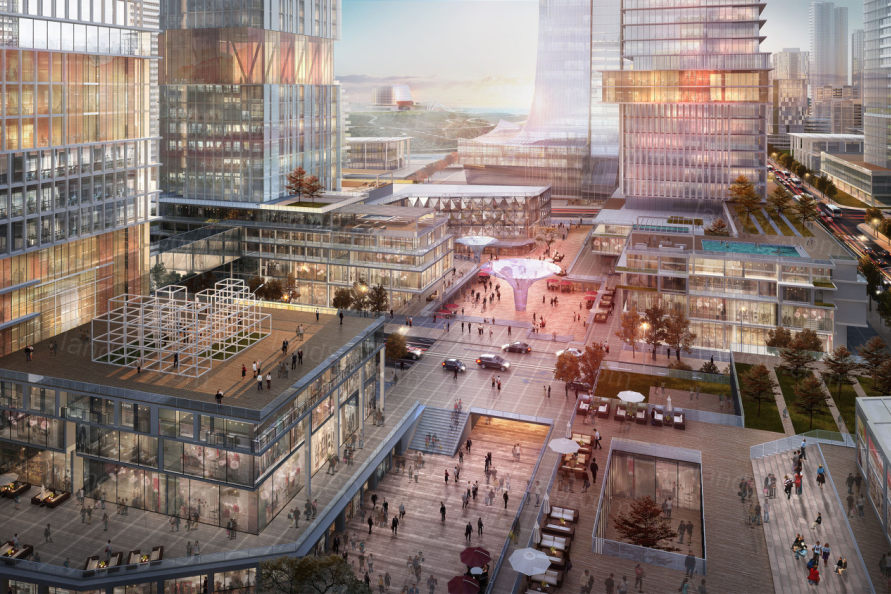

▼地下商业空间无缝连接地铁站与地面活动 Underground commercial space seamlessly link the subway stations to the activity aboveground.

曾经位于市郊的杨春湖地区,由于武汉人口的迅速增长,人居密度迅速上升,但规划与愿景的缺位导致区域无法承载城市的扩张需求。原有的建设占据了湖岸,这样虽然为城市发展赢得了相应空间,但是也导致了区域内的水质恶化。与此同时,位于湖岸的大型垃圾填埋场也是重要的环境隐患。Sasaki的团队针对这些现状条件,提出了五项关键补救策略以应对相应的环境挑战。第一项策略是结合两港公园的建设, 对区域内水道进行系统性梳理与自然化处理。通过软化原有的硬质渠道,设计重塑了水系内的自然过程,相关举措包括:将水系重新连接至湖体泄洪区,调蓄雨水以减少洪涝 的影响,重塑河岸生境,增加人行系统与野生动物生境的连接性等。
The first strategy was the naturalization of the existing canal network throughout the district, along with the ongoing implementation of the wetland park. The formerly channelized waterways are restored to mimic natural processes including reestablishing their connection to the floodplain of the lake, managing stormwater to reduce impacts from flooding, improving the riparian habitat, and enhancing connectivity to the lake for both humans and wildlife. Once on the periphery of the urban core, a recent influx in population to Wuhan led to the rapid densification of the district, but absent a planning vision to accommodate for this growth. Reclamation of the lake’s edge provided necessary land to respond to development pressures, but resulted in a detrimental impact to the water quality. Another significant environmental concern was a large solid waste landfill near the waterfront. These existing conditions inspired the Sasaki team to develop a series of five key remediation strategies that respond to these environmental challenges.
▼地标性的人行桥横跨在现有的湖滨道路上,将中央公园与湖泊连接起来 A landmark pedestrian bridge spans over the existing waterfront roadway and links the central park to the lake.
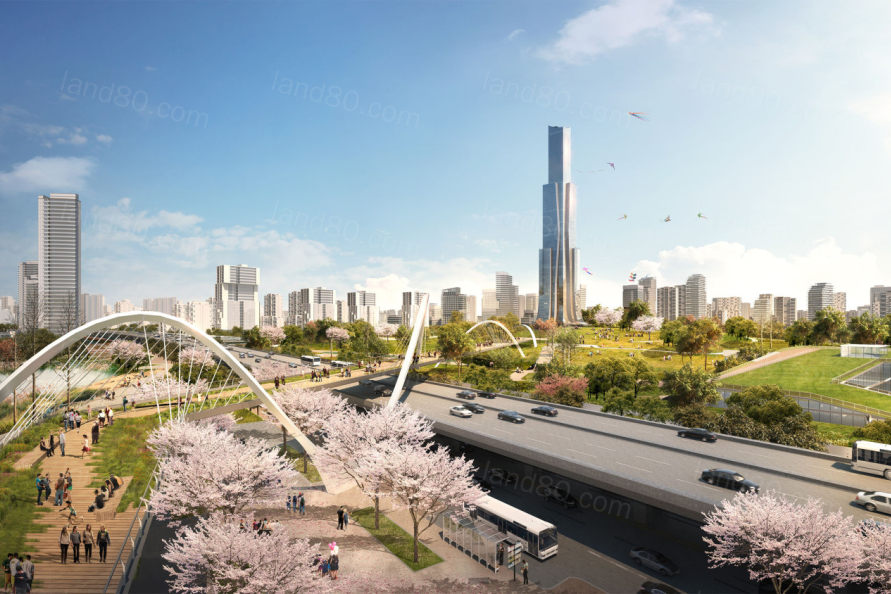

其次,规划沿湖岸设置了一系列人造湿地,这一策略将净化城市地表径流,并为鸟类、两栖类、水生及陆生生物提供多样的栖息地。湿地中还设置了一系列栈道与小径,并与片区内内其他慢行系统相连,创建连续的公共水岸。
Second, a strategy of constructed wetlands along the lake’s edge filters urban runoff while providing critical habitat for a variety of avian, amphibian, aquatic, and terrestrial species. Designed with a series of boardwalks and trails that link to other recreational pedestrian routes throughout the district, the wetland establishes contiguous public access along the once privatized waterfront.
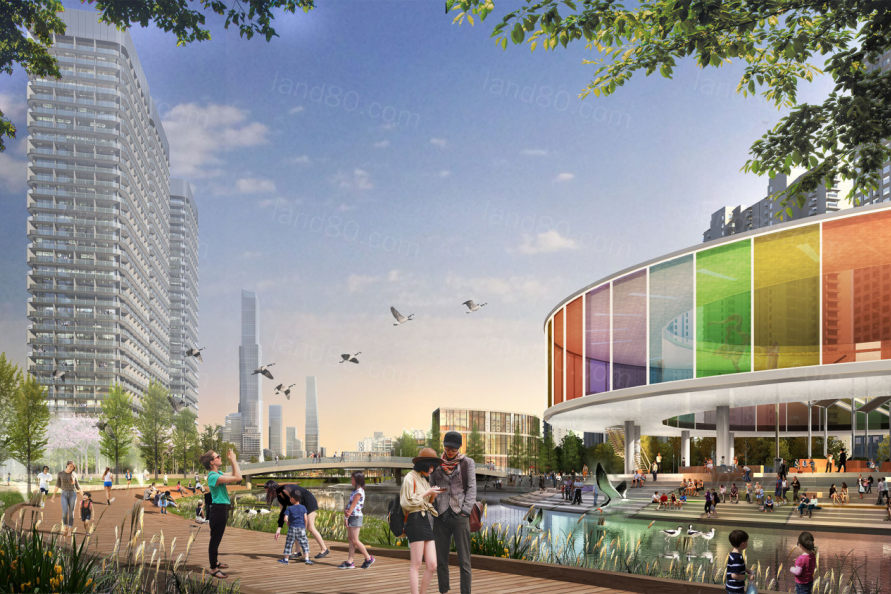
▼区域内的景观提供了多种多样的功能,包括步行空间、休闲娱乐、雨水储存和回灌以及为野生动物提供栖息地 The landscapes throughout the district serve multiple purposes including pedestrian mobility, recreational amenity, stormwater storage and recharge, and wildlife habitat.

第三项策略是在整个区域中,延伸东湖绿道系统。绿道的设置顺应了场地现有水系及主要道路,其创造的城市森林提供了诸多重要功能,包括:动植物生境的营造,通过荫蔽周边建筑以减小能耗,以及为行人提供舒适的微气候等。
The third strategy was the creation of an extended East Lake Greenway system throughout the entire district that follows existing drainage patterns and major roadways. This system provides an urban tree canopy that offers numerous benefits including habitat creation, energy reduction by shading adjacent buildings, and a comfortable microclimate for pedestrians.
▼区域内多样的景观类型,可能包括步行美食街、绿树成荫的休闲空间、雨水花园和生态草沟、裙房上的城市农业以及社区屋顶露台等 Diverse landscapes within the neighborhoods may include pedestrian food streets, shaded recreational spaces, rain gardens and bioswales, urban agriculture atop podiums, and community roof terraces.
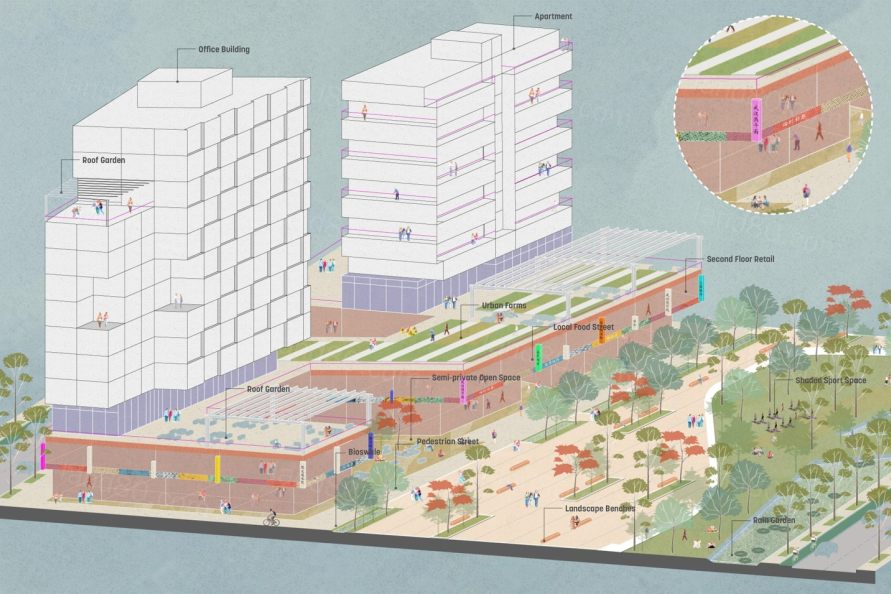
▼中层建筑的设置为引入裙房景观、空中花园和绿色屋顶提供了机会,最大限度地增加了区域内的公共及半公共景观 Mid-rise buildings present opportunities to introduce podium landscapes, sky gardens, and green roofs that maximize the amount of public and semi-public landscapes throughout the district.
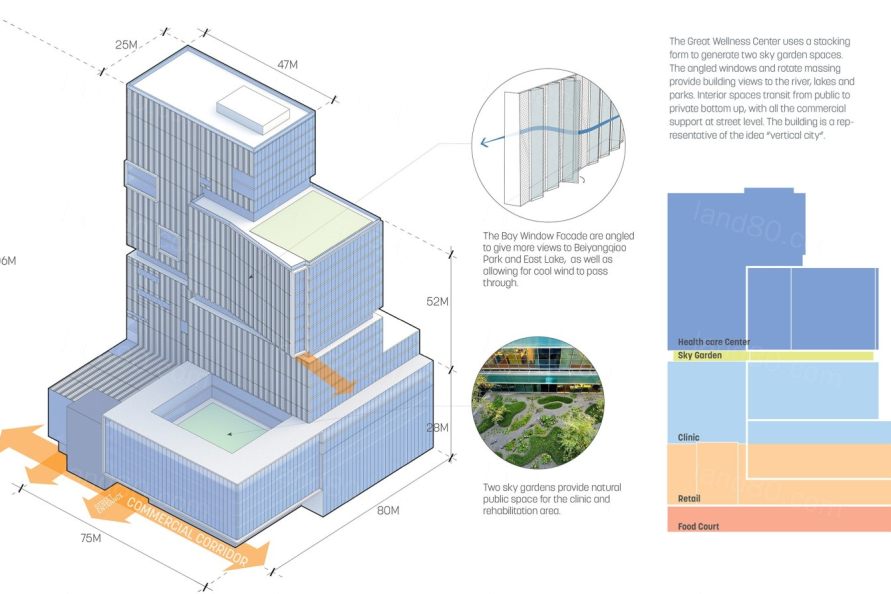
第四,区域内各街区均设置有口袋公园,所有居民均可在 10 分钟内步行到达。口袋公园满足了居民日常休闲的需求,提供游乐场及运动场等设施,于此同时也结合了雨水花园,在收集、清洁地表径流,补充地下水的同时,减少了城市洪涝的风险。最后一项策略,是在原有填埋场的基础上,设置全新的中央公园。设计将曾经令人嗤之以鼻的城市创伤,转变为休闲与生态的活力中心。以上五项策略结合,一共为商务区提供了 368 公顷全新的公共空间。这一公共空间网络连接整个商务区,提供了多样的景观类型,创造了令人 难忘的城市体验。
Fourth, a series of pocket parks are interspersed in each of the district’s neighborhoods, allowing for all residents to live within a 10 minute walk of a public landscape. These pocket parks provide daily amenities such as playgrounds and sports fields while also incorporating rain gardens to collect, filter, and replenish groundwater while reducing the impacts of urban flooding. Finally, the fifth strategy was the creation of a new central park. Built upon a former solid waste landfill, the central park repurposes this once noxious use into a vibrant recreational and ecological amenity. When combined, these strategies provide a total of 368 hectares of new open space throughout the district in a variety of typologies that enhance the urban experience.
▼人行道、商业连廊和线性公园, 联系了区域内的主要开放空间 Most of the 368 hectares of open space are contiguous, linked by a network of pedestrian alleys, arcades, and linear parks.
▼北洋桥公园建设在封顶后的垃圾填埋场上,将过去的城市伤疤转变为赏心悦目的休闲设施。该公园也是平坦的区域内难得的地形体验 The park is built over an existing solid waste landfill after being capped, turning an eyesore into an amenity. The park is also one of the rare opportunities experience some topography within the otherwise flat district.
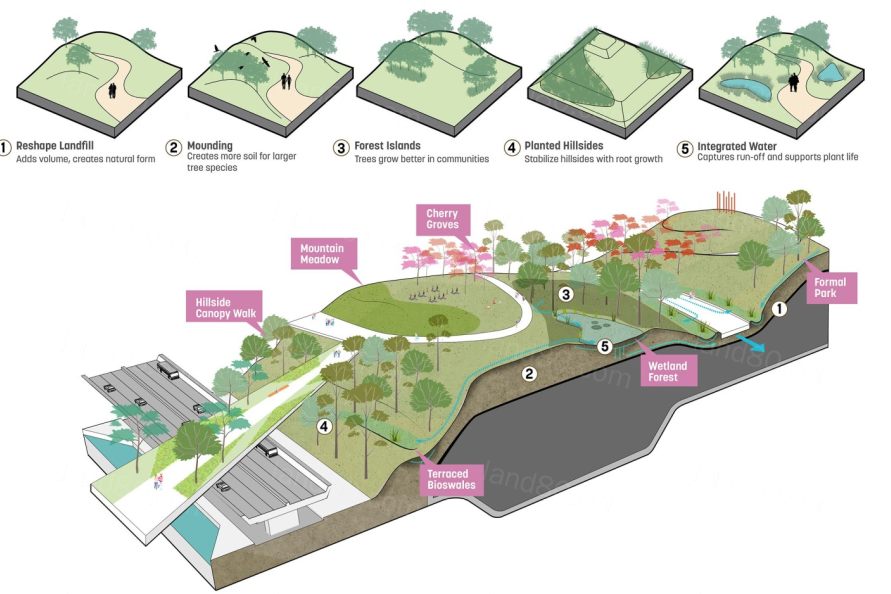
由环境改进措施及景观干预手段构成的绿网结构,将整个商务区紧紧整合其中。规划进一步设置了全面的慢行系统网络,创造了更加安全的,符合人尺度的步行环境,并将区域内的公园、广场、街道空间整合其 中。南北向的街道及线性公共空间,将区域内景观连接至湖区,使市民可以更舒适地到达湖岸,并在城市中创造了视觉通廊。
With the environmental improvements and landscape interventions providing the initial armature for the new district, the plan was then organized around a comprehensive pedestrian network to promote walkability and a safer, human-scaled environment that links the district’s parks, plazas, and streetscapes. A series of north-south streets and linear open spaces connect interior landscapes to the lake, providing accessibility and establishing view corridors.
▼由中央公园向外辐射的城市街区优化了考虑人行可达性,将外围街区与商业核心区连接起来Urban blocks that radiate outwards from the central park prioritize pedestrian connectivity, linking the outer neighborhoods to the commercial core.
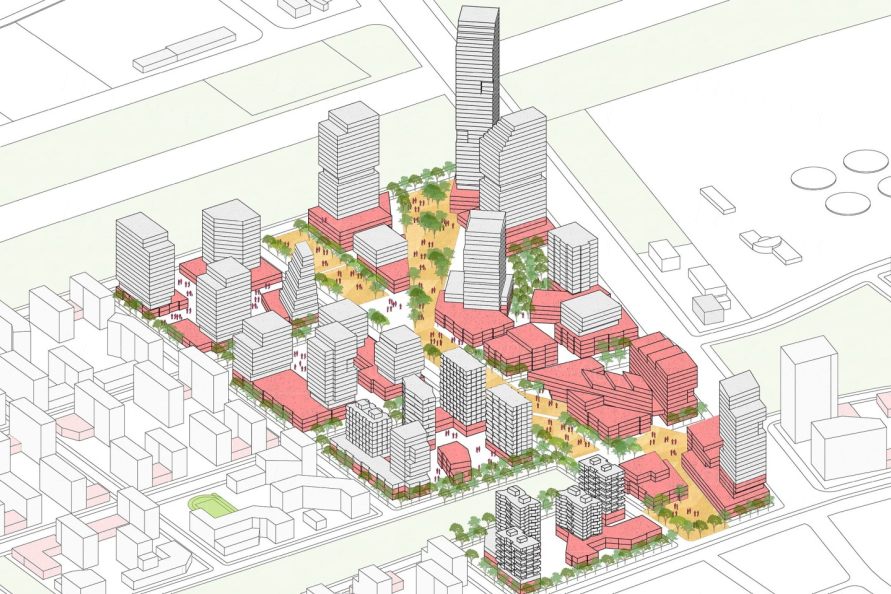
▼通过对不同人群的分析与设想 图片展示了不同人群如何使用本区域及其中设施 Hypothetical itineraries indicate how different groups of people might move through the district and the amenities that they would use.
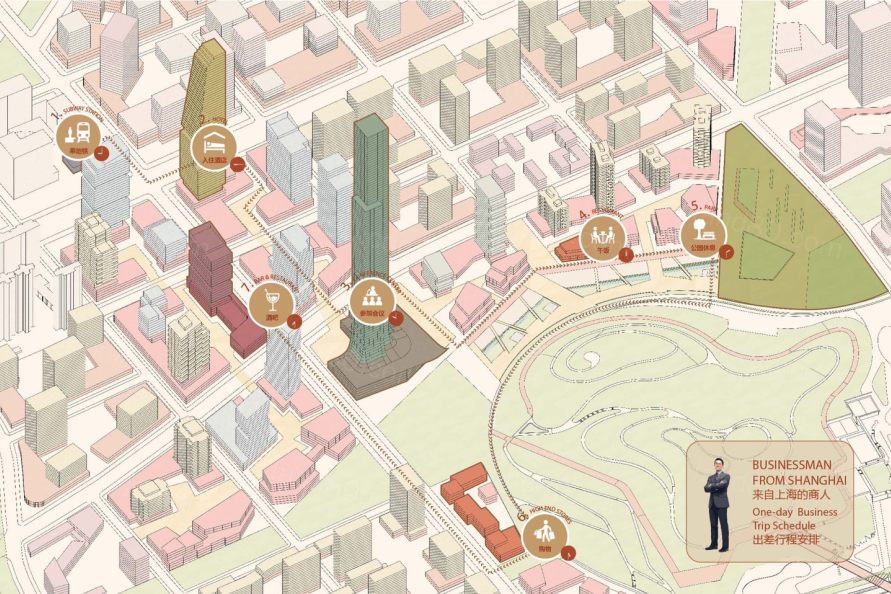
▼创业者一天的行程表 An itinerary illustrating how an entrepreneur might spend a day in the district

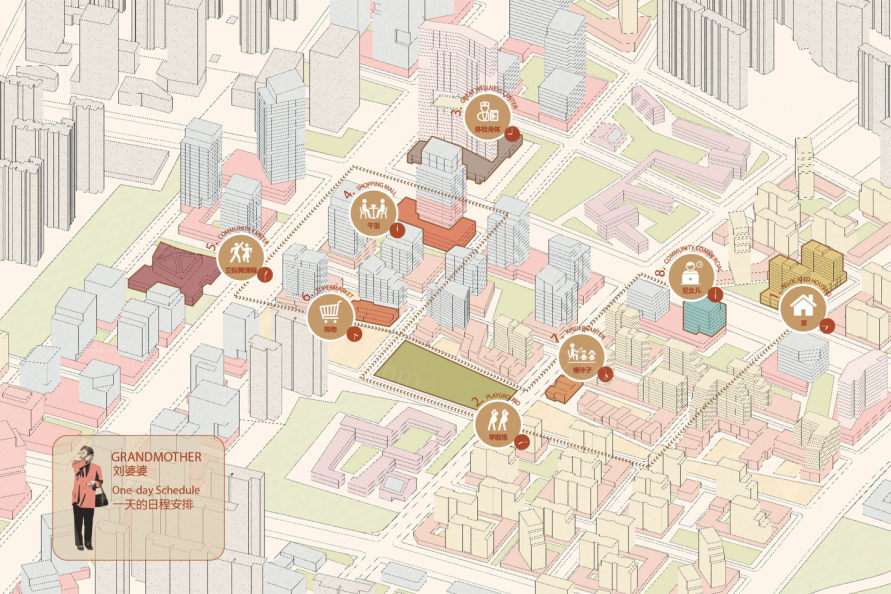
▼区域内居民的典型行程表 A typical itinerary of a resident of the district.
▼尺度的城市街区强调步行体验,而连廊的设置则便于行人到达中央公园 Smaller urban blocks promote walkability and arcades facilitate pedestrian connectivity to the central park.
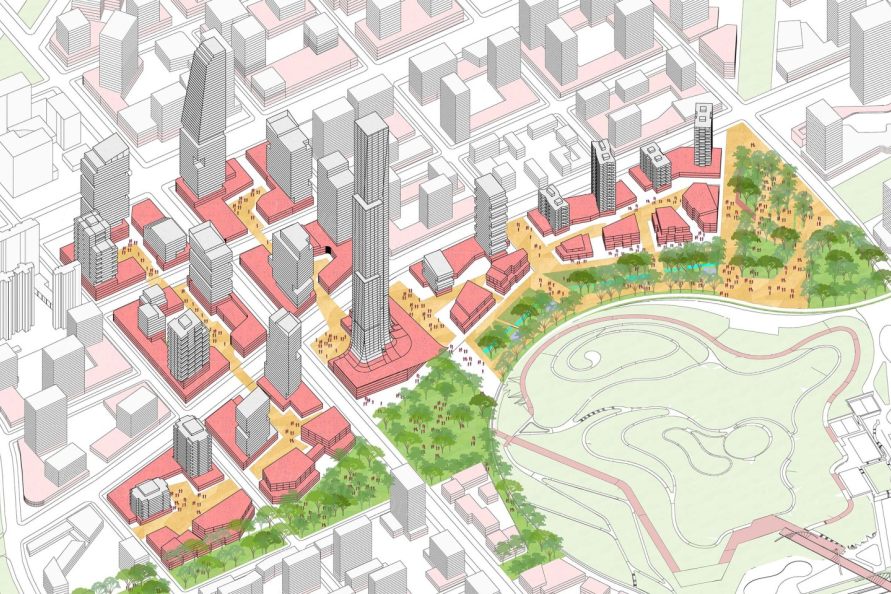
区域采用了高密度小街区的道路网络,并为未来的出行模式提供了相应路径,一系列举措构造了系统的城市设计策略。规划精心考虑了如何保留原有的居住区,减少对现有社会网络的破坏;与此同时提供了优化导则,在现有住区内部创造更丰富的土地利用类型。这一导则在为现有居民提供更多工作机会的同时,也为区域未来发展留有余地。规划绘制一份以景观环境为纲的城市蓝图,在对生态环境的积极动议中,定义了武汉发展的新世代。
Densifying the street grid to create smaller blocks and accommodating autonomous vehicle routes completes the urban design interventions the district. The master plan thoughtfully retained existing neighborhoods to avoid disrupting social networks, while providing guidelines for diversifying land uses within parcels to foster new business opportunities for local residents and allowing for flexibility to accommodate future uses as the district evolves. The result is a landscape-forward urban blueprint that advances an environmentally progressive agenda and defines Wuhan’s next generation of growth.
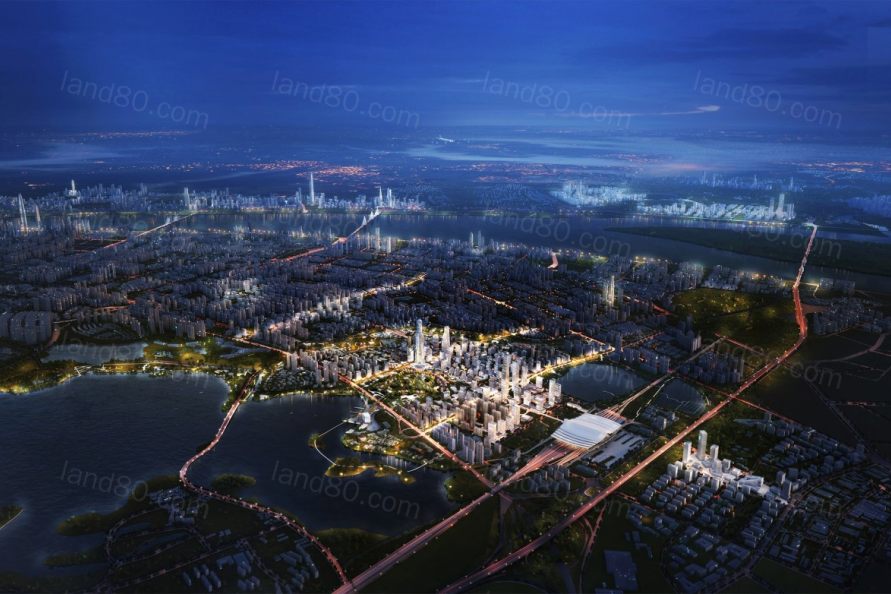
▼杨春湖中央商务区为武汉市创造了一个引力核心,凸显了武汉市对交通导向型发展和可持续发展的城市承诺 The Yangchun Lake Central Business District creates a new center of gravity in Wuhan and accentuates the city’s commitment to transit-oriented development and sustainable urbanism.

项目名称:武汉杨春湖商务区
设计单位:Sasaki
项目地址:中国武汉
客户名称:武汉市规划研究院, 武汉市自然资源和规划局
项目面积:1,800 公顷 (4,448 英亩)
服务范围:城市规划、城市设计、景观建筑
Project name: Wuhan Yangchun Lake Business District
Architect: Sasaki
Project location: Wuhan, China
Client name: Wuhan Planning & Design Institute, Wuhan Nature Resource and Planning Bureau
Size: 1,800 Hectares (4,448 acres)
Status: Completed 2018
Services: Planning and Urban Design, Landscape Architecture
|