位于中国深圳市罗湖区的一所公立中小学新建项目,依山层层退台,与山林融为一体。
This
is a project to build a new public primary and secondary school for children
aged 7 to 15 in Luohu District, Shenzhen, China.
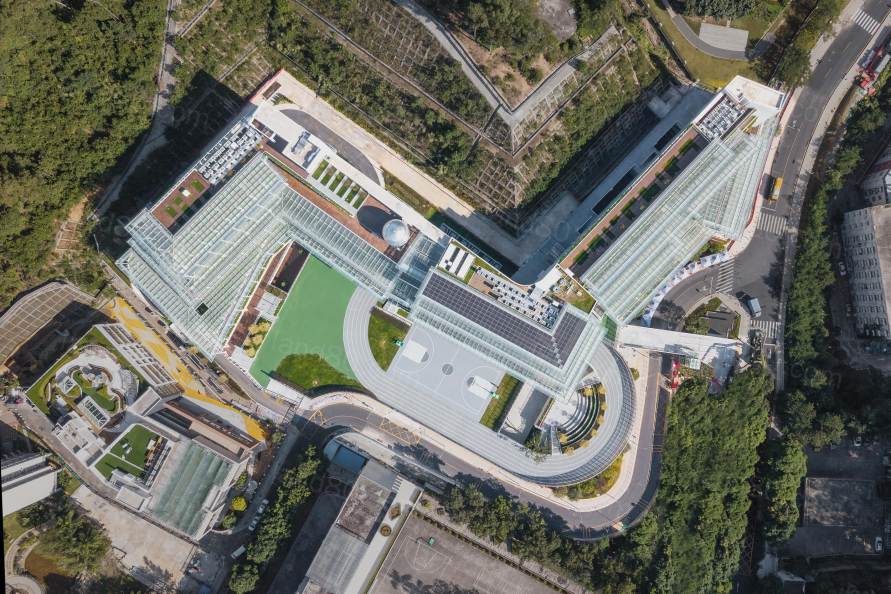



目前,越来越多的新建学校以“未来”为主题,日比野设计在考虑设计之前,会先思考对孩子们来说“未来”的意义是什么,面向“未来”,要在学校里学习怎样的知识。由此,以培养可持续社会基础的Education for Sustainable Development(可持续发展教育)目标与我们以往的理念不谋而合,现代社会需求的新式教育是引导学生能够独立面对自我,关心社会问题,实施自主的、对话交流式的深刻学习。作为学校环境来说,“未来”并非指一味地使用高科技设备,我们认为的“未来学校”,应该是目标朝向可持续社会,关注生活中与生产基础相关的低科技要素,有意识地了解地球环境影响因素等。我们尽可能多地把自然元素引入进学校环境,“以自然与交流为中心的多样化习场”作为设计概念,实现促进学生自主思考、能动学习的可持续性未来学校。
The themes of the new schools were what the
'future' should look like for children and how they should learn for the
'future'. In order to achieve a sustainable society, education for sustainable
development (ESD) has been a focus in education in recent years. ESD requires
learning that encourages deep learning in a proactive and interactive way about
contemporary society and one's own problems, and the use of high-tech is not
the only 'future', but awareness of low-tech and environmental issues can lead
to a sustainable society. In this project, the place to learn about this is
considered to be the 'School of the Future', and based on the design concept of
a 'diverse learning place with nature and communication at its core', the
following methods were used to achieve a school that encourages independent
thinking and learning among the students.


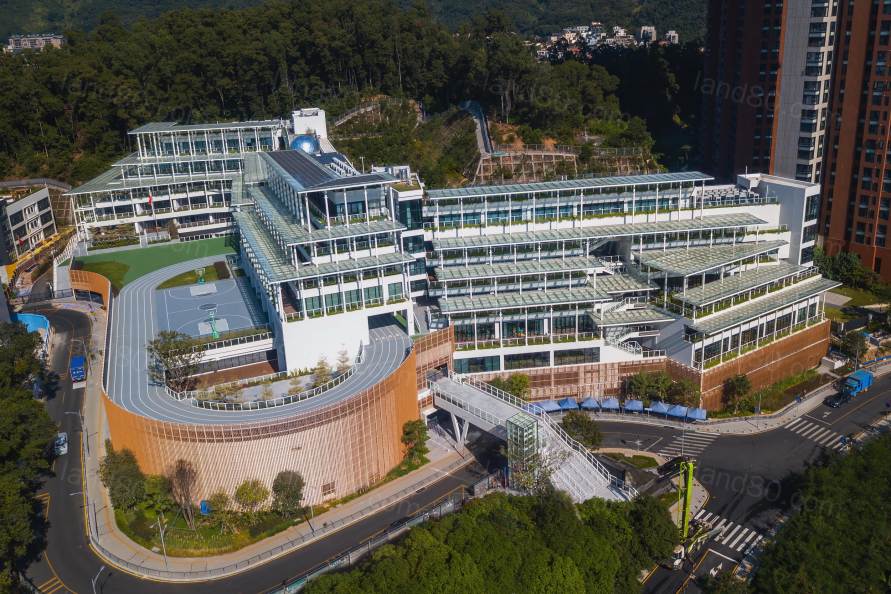
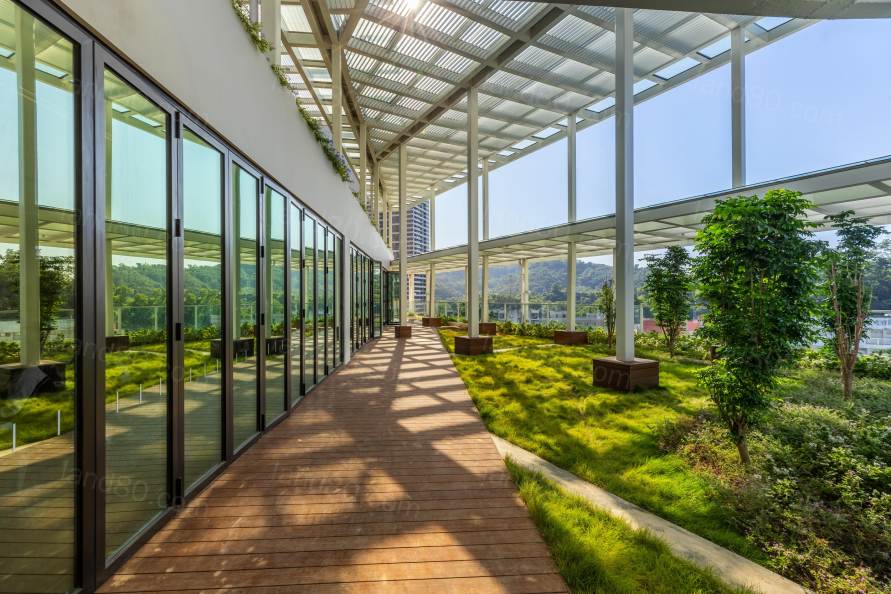
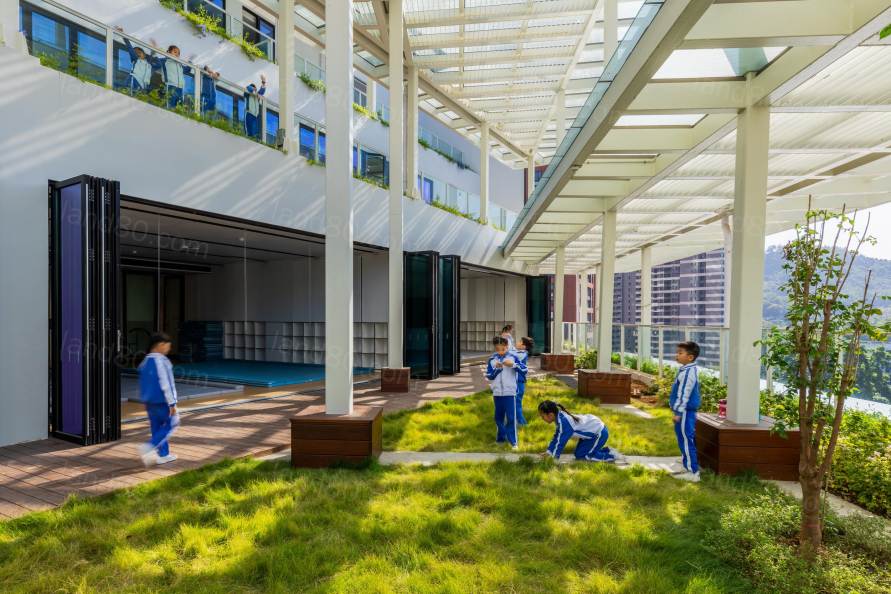
因占地限制要求,建筑需要切割部分山体,但我们不想把山夷为平地,而是选择结合山的形状,通过退台来实现学校由山而生的效果。切割山体而遗失的大树,通过倾斜的阶梯状建筑造型,得以重新移植在地上楼层的种植带上,并补充新的灌木植物。由于斜面处理,每个教室都能保证充足的阳光,从而方便打造自然的阳台。学生们下课后的休息时间里,可以到班级专属的阳台上种花浇水、与隔壁班的朋友聊天、与上下层不同年级的校友交流。此外,宽敞的开放式走廊跳跃出了“走廊”的框架,与教室连为一体,成为新的学习场所,同时摆放了能自由组合的家具和书柜,跨越班级间隔,促进多样化的学习和身体活动。
Due to site constraints, it was decided to
construct the building by cutting away part of the original mountain, but in
order to restore as much as possible the trees lost during the cutting, a
planting strip including medium and tall trees was planted in the school
building, creating a new slope that is integrated with the existing mountain
forest. The school building has a stepped cross-sectional configuration along
the existing slope, and each classroom has a terrace that receives plenty of
sunlight, creating a pleasant space where the sun shines through the trees. A
small waterfall, which takes advantage of the difference in elevation, provides
a place of relaxation where students can cool off while listening to the sound
of the water. These natural terraces, which make the most of the site's
features, allows children to communicate beyond the confines of their class and
grade level.

▽阳台


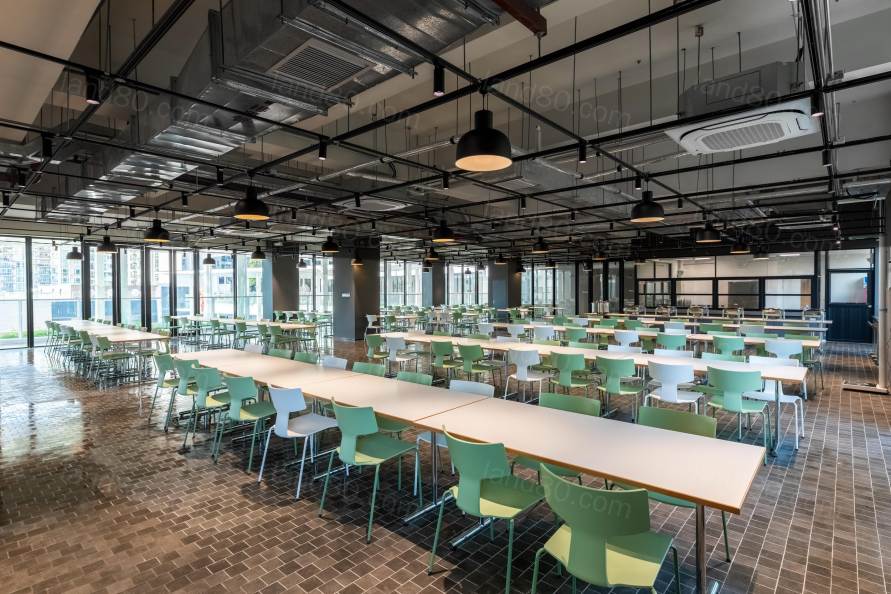
▽餐厅

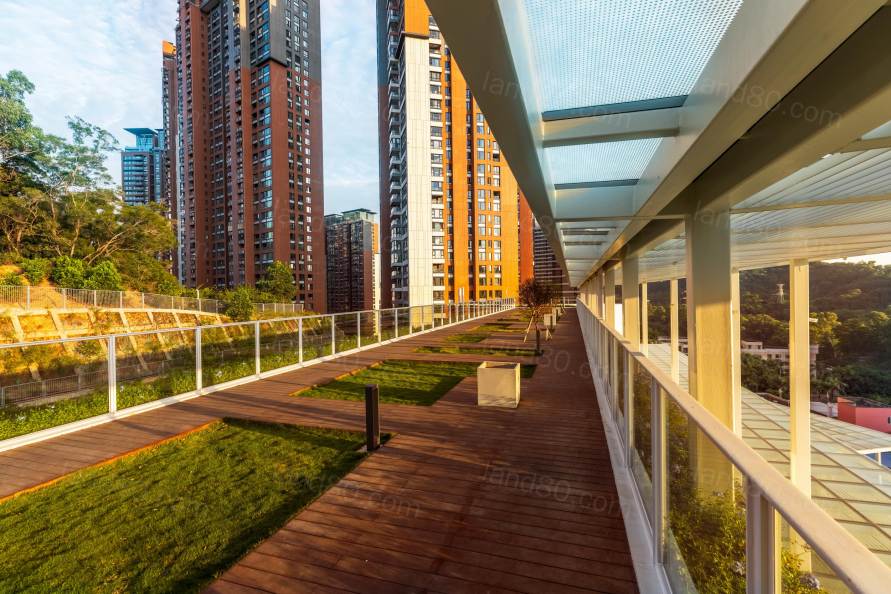
▽用途广泛的宽阔走廊

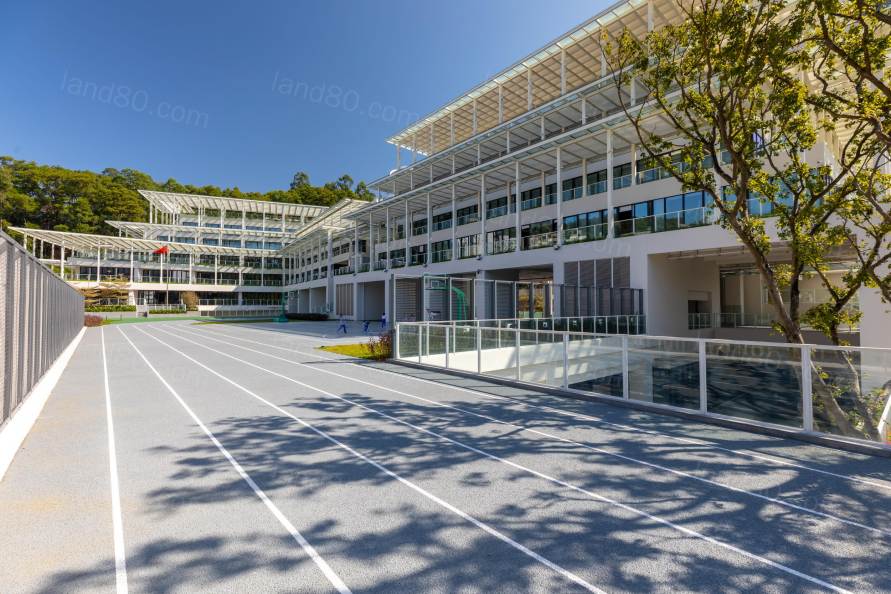
我们利用建筑的台阶高差,制作了一个迷你水景,为体现水往低处流的自然现象。深圳是一个降雨较丰沛的城市,因此我们在操场设计时也和传统不同,将跑道贯通了建筑的一部分,做出建筑平台下的阴影空间,即使是雨天也可以完成小规模的户外活动课程。另外,切割山体而保留下来的部分岩石展示在学校最底层的阳台上,除了自然氛围的营造作用以外,岩石内部材质的外露,可以成为引发孩子们对地质学研究产生兴趣的契机。即使是地下楼层,利用与道路的标高,同样充分地满足了采光要求。
The terrace at the bottom of the basement
is designed to display rocks left behind in the process of carving the
mountain, showing the real rock surfaces, which will lead to geological studies
and allow children to get in touch with the original appearance of the land.
Dry areas and atriums have been built to ensure that even the basement floors
are well lighted with the use of natural energy. Unlike conventional corridors,
the corridors are wide and open, as they are seen as one of the new learning
spaces that are integrated with the classrooms. The arrangement of freely
combinable furniture and bookshelves there encourages diverse learning and
activities across the class. Also, taking into account the rainy nature of the
area and the strong summer sun, the ground was designed so that, unlike
conventional outdoor grounds, part of the ground is inside the school building.
By this way, a semi-outdoor space is created in a part of the ground, allowing
people to exercise even when it rains or when the sun is strong.

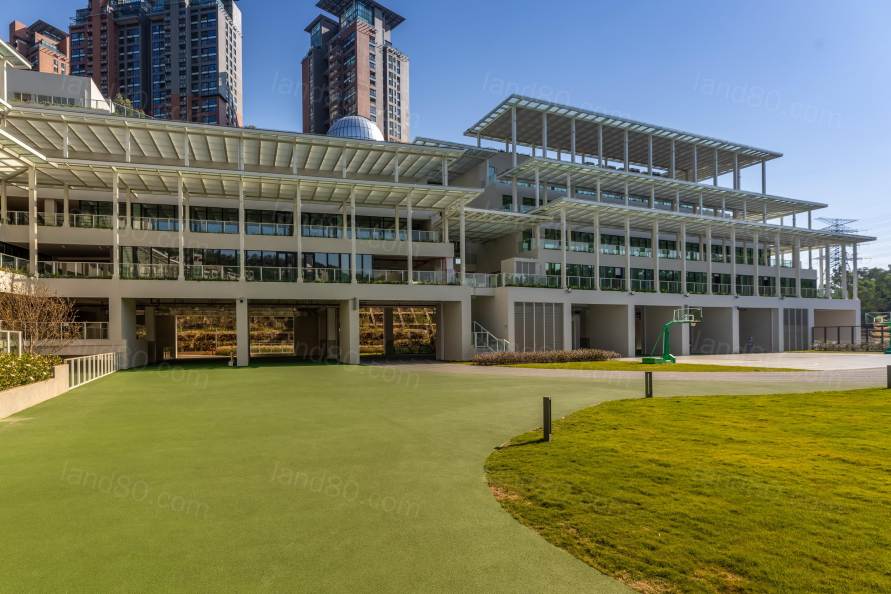
▽活动空间
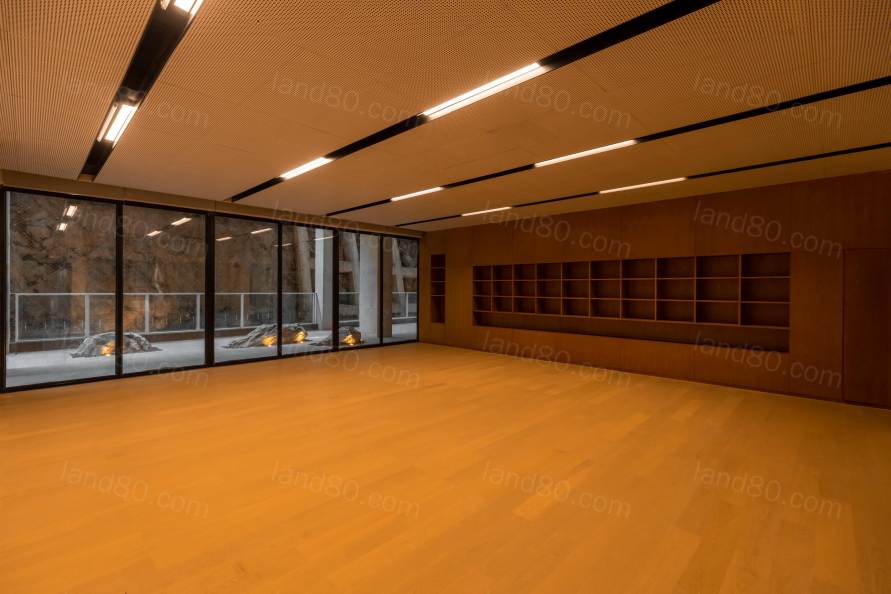


整个设计以可变的空间为主,不限定学习的场所和形式,同时将光、风、水、石、植物等自然元素点缀在学校的各个位置,任何场所都是学习行为发生的新时代“习场”。在这所未来学校的孩子们,能够从课堂的知识学习中延伸而出,自主地思考自我及社会的各种问题,达到实践能力的同步发展。设计从环境去促进能动性的学习方式及探究式的学习过程,以落实可持续发展的教育理念。This flexible space does not limit the form
of learning, and natural elements such as light, wind, water, stones and plants
are scattered throughout the school building to create a 'new learning place'
where learning can exist wherever children are. By developing the ability to go
beyond knowledge and put it into practice through exploratory learning,
Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) is achieved, and the school is a
'school of the future' where children are encouraged to think independently
about their own and society's problems and learn to take action.
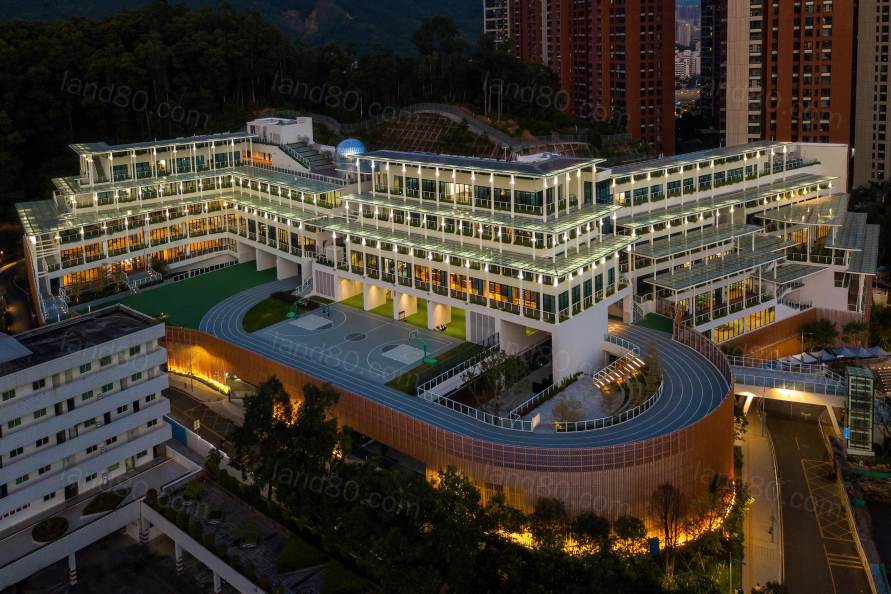
▽夜景


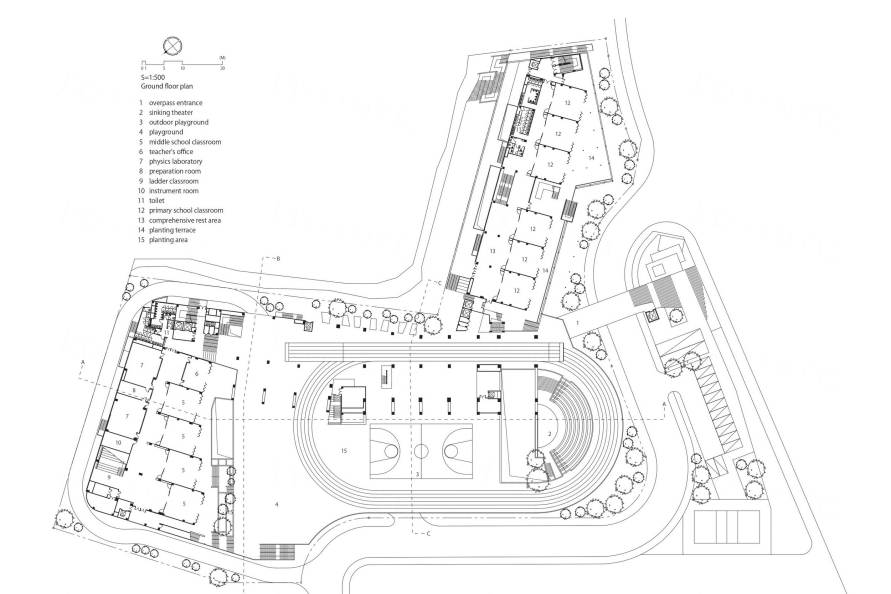
▽平面图
▽剖面图
项目名称:LUOHU FUTURE SCHOOL
项目地点:广东省深圳市
方案设计:HIBINOSEKKEI + youji no shiro、深圳市纯粹实践设计咨询有限公司(PURE&PRACTICE)
施工图设计:深圳壹创国际设计股份有限公司 (YICHUANG)
代建单位:华润(深圳)有限公司 (China Resources)
占地面积:14,000.0㎡
建筑投影:6,000.0㎡
使用面积:42,000.0㎡
结构规模:混凝土+钢结构、地下4层、地上5层
竣工时间:2021年9月
照片拍摄:IVAN CHO
Project
name:SLF Primary and Secondary School
Address: Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Design: HIBINOSEKKEI + Youji no Shiro + PURE&PRACTICE
EPC: YICHUANG
Construction
agency: China Resources (shenzhen) Co., Ltd.
Site area: 14,000.0㎡
Building
area: 6,000.0㎡
Floor
area: 42,000.0㎡
Construction: RC+Steel,5 stories above ground 4 stories below ground
Number of floors: 2 floors
Completion: September 2021
Photo credit: IVAN CHO
|